All Categories
Featured
2 people acquisition joint annuities, which give a surefire earnings stream for the remainder of their lives. If an annuitant passes away during the circulation period, the remaining funds in the annuity might be handed down to a marked recipient. The particular choices and tax effects will depend upon the annuity agreement terms and applicable legislations. When an annuitant passes away, the interest made on the annuity is dealt with differently depending upon the kind of annuity. Most of the times, with a fixed-period or joint-survivor annuity, the rate of interest proceeds to be paid to the making it through recipients. A survivor benefit is a function that guarantees a payment to the annuitant's beneficiary if they pass away before the annuity repayments are exhausted. The accessibility and terms of the fatality benefit might differ depending on the particular annuity contract. A kind of annuity that quits all repayments upon the annuitant's fatality is a life-only annuity. Understanding the terms and conditions of the survivor benefit prior to buying a variable annuity. Annuities go through taxes upon the annuitant's death. The tax obligation treatment depends on whether the annuity is kept in a certified or non-qualified account. The funds undergo earnings tax in a certified account, such as a 401(k )or individual retirement account. Inheritance of a nonqualified annuity normally causes taxation just on the gains, not the whole quantity.

The original principal(the amount originally deposited by the parents )has actually currently been taxed, so it's exempt to tax obligations once again upon inheritance. Nevertheless, the profits part of the annuity the passion or financial investment gains accrued in time undergoes income tax. Usually, non-qualified annuities do.
have actually passed away, the annuity's benefits usually revert to the annuity proprietor's estate. An annuity owner is not lawfully called for to educate present recipients regarding modifications to recipient classifications. The choice to change beneficiaries is usually at the annuity proprietor's discretion and can be made without informing the present beneficiaries. Considering that an estate practically doesn't exist until a person has passed away, this recipient classification would just enter result upon the fatality of the named individual. Generally, as soon as an annuity's owner passes away, the assigned recipient at the time of fatality is entitled to the advantages. The partner can not transform the beneficiary after the owner's death, also if the beneficiary is a minor. Nonetheless, there may be certain provisions for managing the funds for a minor recipient. This frequently involves selecting a lawful guardian or trustee to manage the funds until the youngster gets to adulthood. Normally, no, as the beneficiaries are not accountable for your debts. It is best to speak with a tax professional for a details answer relevant to your case. You will continue to receive settlements according to the agreement timetable, yet trying to get a lump sum or loan is likely not an option. Yes, in nearly all cases, annuities can be inherited. The exemption is if an annuity is structured with a life-only payout choice via annuitization. This sort of payment discontinues upon the death of the annuitant and does not give any recurring worth to successors. Yes, life insurance coverage annuities are normally taxable
When withdrawn, the annuity's revenues are strained as ordinary revenue. Nevertheless, the principal amount (the initial investment)is not taxed. If a recipient is not named for annuity advantages, the annuity proceeds normally most likely to the annuitant's estate. The distribution will certainly follow the probate process, which can delay settlements and may have tax effects. Yes, you can call a trust fund as the recipient of an annuity.
Long-term Annuities and inheritance tax
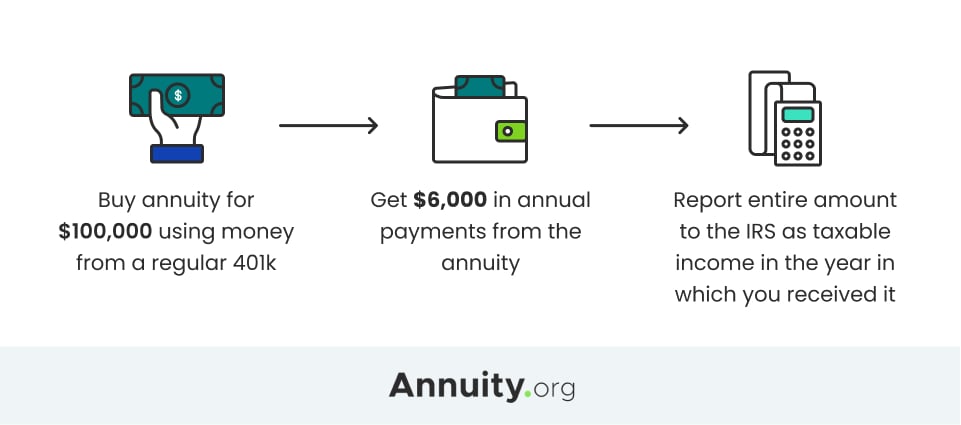
Whatever portion of the annuity's principal was not already exhausted and any type of profits the annuity built up are taxed as revenue for the beneficiary. If you acquire a non-qualified annuity, you will just owe taxes on the incomes of the annuity, not the principal made use of to purchase it. Because you're receiving the whole annuity at when, you need to pay tax obligations on the whole annuity in that tax obligation year.
Latest Posts
Highlighting the Key Features of Long-Term Investments Everything You Need to Know About Financial Strategies Defining Variable Annuities Vs Fixed Annuities Features of Smart Investment Choices Why Fi
Highlighting the Key Features of Long-Term Investments Key Insights on Variable Vs Fixed Annuity Defining Indexed Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity Benefits of Indexed Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity Why What Is A Va
Exploring the Basics of Retirement Options Everything You Need to Know About Deferred Annuity Vs Variable Annuity Defining the Right Financial Strategy Features of Smart Investment Choices Why Choosin
More
Latest Posts